Now accepting applications for WashU Medicine Bold Pioneer Award! (Links to an external site)
The goal of the $10,000 WashU Medicine Bold Pioneer Award is to recognize and encourage early career investigators who have demonstrated bold, pioneering research that is high-risk by virtue of being fundamentally different from standard approaches. The intent is to encourage scientific research investigators to challenge status quo approaches by developing fundamentally different methods, approaches, […]
New blood tests can help diagnose Alzheimer’s — but some aren’t as accurate as others (Links to an external site)
Now that there are drugs to treat Alzheimer’s, blood tests to detect it will likely become an attractive, low-cost option to decide who can get treatment. Some tests are more accurate than others.
Sleeping pill reduces levels of Alzheimer’s proteins (Links to an external site)
Two doses of an FDA-approved sleeping pill reduced levels of Alzheimer’s proteins in a small study of healthy volunteers led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The study hints at the potential of sleep medications to slow or stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, although much more work needs to be done to confirm the viability of such an approach.
Bateman to receive lifetime achievement award (Links to an external site)
Bateman has been chosen to receive the honor for his groundbreaking work in Alzheimer’s research, including the development of plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer’s diagnostics. He will receive the award in October at the Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease conference in Boston.
WashU, Eisai form drug discovery collaboration (Links to an external site)
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the pharmaceutical company Eisai Co. Ltd., headquartered in Japan, have formed a research collaboration aimed at developing new treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions. The two organizations previously have partnered on Alzheimer’s clinical trials, and the new alliance combines their complementary efforts to identify and validate biomarkers and drug targets for a range of neurodegenerative conditions, with a goal of developing new drugs for the benefit of patients worldwide.
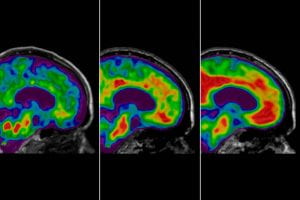
Diagnostic marker found for deadly brain disease marked by dementia, movement problems (Links to an external site)
Sato and Horie led a team that discovered a biomarker for a rare, deadly brain disease known as corticobasal degeneration (CBD). The biomarker could accelerate efforts to develop treatments for CBD.
New center’s aim: to ID biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases (Links to an external site)
A new center established at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis aims to accelerate research into biomarkers of neurodegenerative conditions such as Huntington’s and Parkinson’s diseases, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis (MS) and the so-called tauopathies, a group that includes Alzheimer’s disease along with rarer diseases such as frontotemporal dementia, corticobasal syndrome […]
Blood test for Alzheimer’s highly accurate in large, international study (Links to an external site)
“A blood test for Alzheimer’s provides a huge boost for Alzheimer’s research and diagnosis, drastically cutting the time and cost of identifying patients for clinical trials and spurring the development of new treatment options,” Bateman said. “As new drugs become available, a blood test could determine who might benefit from treatment, including those at very early stages of the disease.”
Alzheimer’s Blood Test: An expert panel with WUSTL (Links to an external site)
Scientists have devised a blood test to detect proteins that form the plaques in the brain that are suspected to cause Alzheimer’s. They believe this may lead to being able to diagnose Alzheimer’s before showing symptoms.
Washington University in St. Louis Leads International Alzheimer’s Clinical Trial to Test Tau Drugs
An international clinical trial aimed at finding treatments for Alzheimer’s disease has expanded to include investigational drugs targeting a harmful form of the brain protein tau. Originally focused on amyloid-based therapies, the trial launched with funding from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 2013. Source: HEC Media